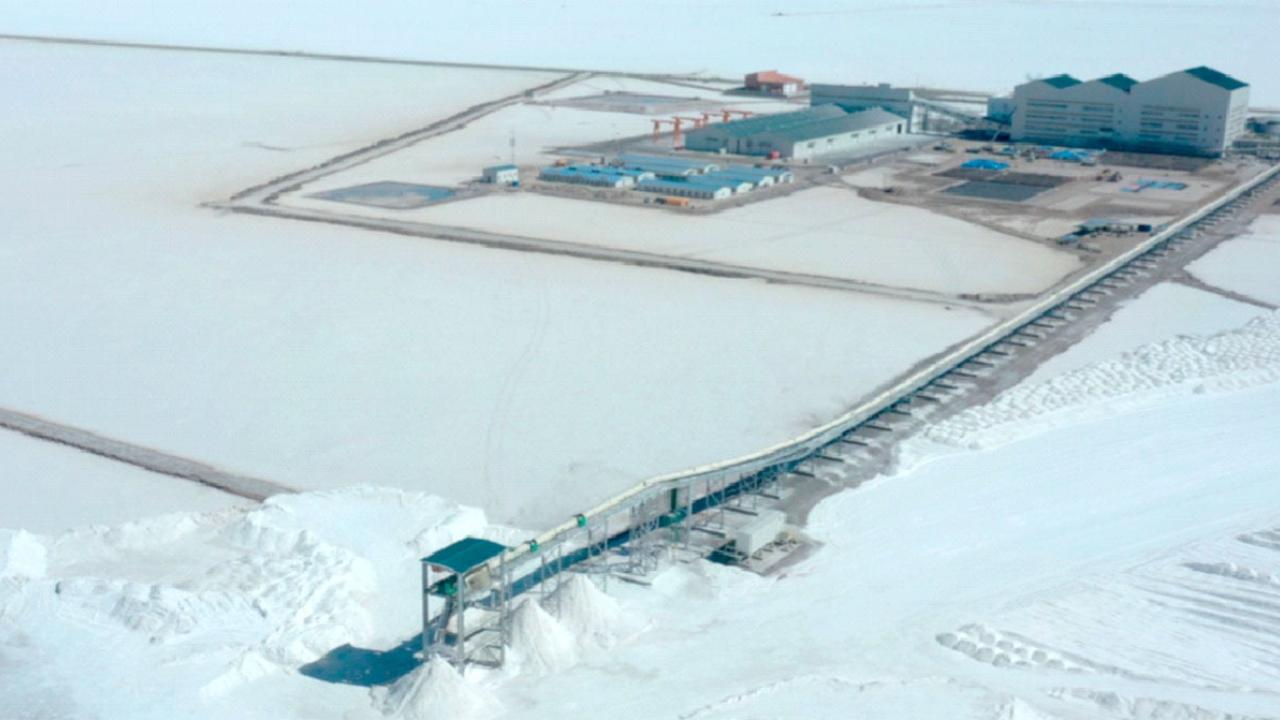
The activity is carried out in 88 production wells in the Salar de Uyuni, 70 in Coipasa (Oruro) and 20 in Pastos Grandes (Potosí).
Yacimientos de Litio Boliviano (YLB) carries out the monitoring and control of 178 production wells in the Uyuni and Pastos Grandes salt flats, in Potosí, and in Coipasa, Oruro, in accordance with the work schedule and within the framework of technical operations established in the territory of Bolivia.
The supervision and control work seeks to determine the variability of concentration and levels of the aquifers. The activity is carried out in 88 production wells in the Salar de Uyuni, 70 in Coipasa and 20 in Pastos Grandes.
“This week the monthly monitoring of the production wells of the three salt flats in the country in which lithium recovery, production and industrialization work is currently being carried out is carried out. We work for industrialization with responsibility towards our Mother Earth,” mentions a YLB report.
According to YLB, the industrialization of lithium can go hand in hand with the responsible use of water and care for the environment.
The construction of the Water Treatment Plant, the agreement with Uranium One Group, and the agreement with the French Geological and Mining Research Office (BRGM), constitute three major milestones in the responsible use of reserves. aquifers.
WATER
According to the Ministry of Hydrocarbons and Energy of Bolivia, it has been demonstrated that it is possible to carry out strategies for the rescue, production and transformation of lithium, without irreversibly affecting water reservoirs and the ecosystem.
He says that Bolivia takes into account environmental care and the protection of aquifer resources, which is why it prioritizes the development of the direct lithium extraction (EDL) method, with which water flows, fulfills its purpose, is recycled and reuse, optimizing use and exploitation.
Although the Llipi Carbonate Plant works through brine pools, its optimization in terms of water use goes hand in hand with the Water Treatment Plant.
Next to the Lithium Carbonate Plant, the Industrial Water Treatment Plant is implemented, a fundamental complementary infrastructure in the lithium production and industrialization process.
It will be one of the largest in Latin America, as it will have more than 35 kilometers of aqueducts, eight wells and a treatment capacity of around 350 cubic meters.