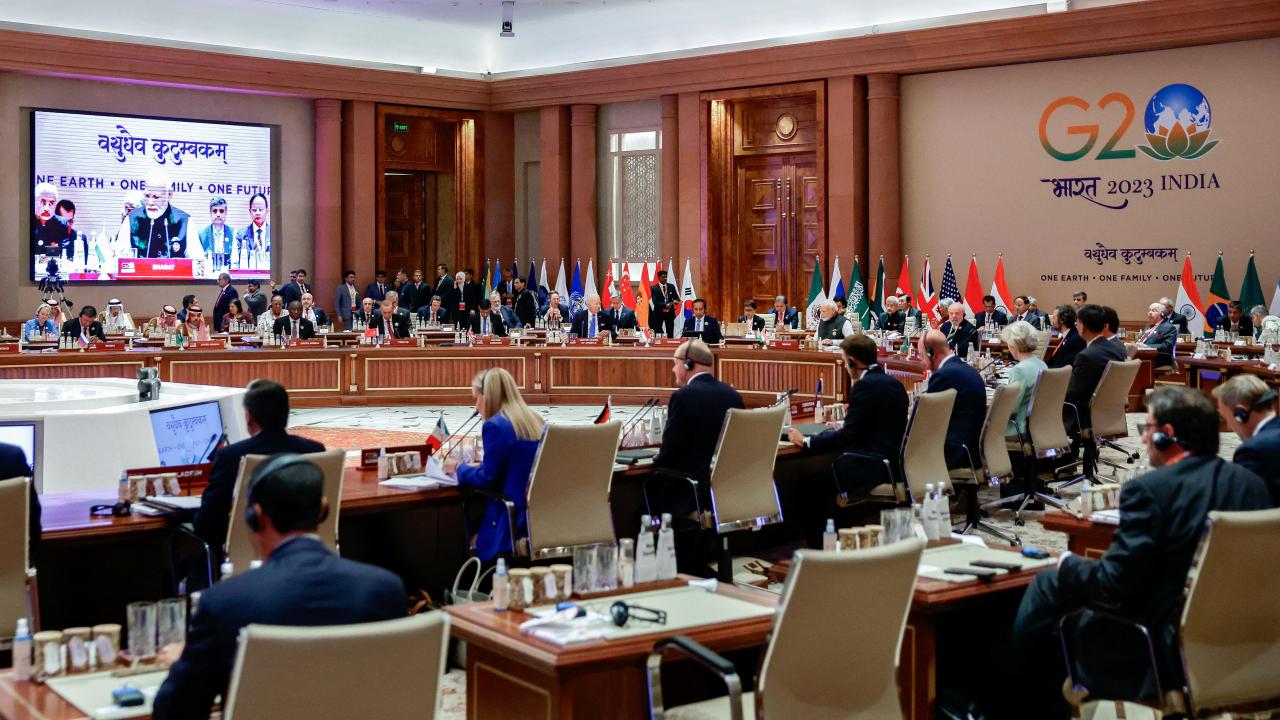
According to the US consultancy, a soft landing appears to be within reach for several advanced economies due to effective policy maneuvering, improved supply-demand balances and good fortune, such as mild winters in Europe.
The latest report from the American consulting firm Moody's on the global macroeconomic outlook for 2024 is blunt. The world economy is moving towards a post-pandemic equilibrium with a constant normalization of economic activity in the main advanced and emerging markets.
Under this scenario, a soft landing appears to be within reach for several advanced economies due to effective policy maneuvering, improved supply-demand balances, and good fortune, such as mild winters in Europe.
In addition to a strong US economy (negative Aaa), sustained and stronger-than-expected post-pandemic recoveries in several emerging market countries offer a constructive growth outlook.
For their part, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Bank (ECB) will likely begin reducing rates in the second quarter. Geopolitical risks and inflation remain as potential threats to the outlook.
Likewise, the consulting firm predicts that the global production and trade panorama will evolve along with geopolitical changes. To be specific, the report details three important projections:
- G-20 global growth will likely decline from 2022 and 2023 levels:
The G-20 economies would collectively expand by 2.4% in 2024 and 2.6% in 2025, compared to 2.9% in 2023. While the G-20 advanced economies will slow by 1.8% in 2023 to 1.5% in 2024 and 1.6% in 2025. Growth in G-20 emerging market countries is estimated at 3.8% this year and 3.9% in 2025, after the 4.7% in 2023.
- G3 central banks are on track to reduce and normalize rates:
The world's major central banks will begin normalizing monetary policy in due course, provided inflation remains on a downward path. Moody's maintains the expectation that the Fed will reduce the federal funds rate by a cumulative total of 100 basis points in 2024, bringing it to 4.25%-4.50%, and will cut it further in 2025.
The ECB is also expected to begin policy normalization in the second quarter. As the Bank of Japan (BoJ) seeks to normalize monetary policy and move away from negative interest rate policy and yield curve control, soft inflation could delay the process.
- Macroeconomic risks have decreased compared to last year, while geopolitical risks are prominent:
Key macroeconomic and financial risks that remain on the consultancy's radar include inflation, uncertainty over the level of terminal interest rates and points of vulnerability within the financial sector.
Geopolitical developments continue to pose risks to commodity markets and global trade. The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine, conflicts in the Middle East and tensions in Asia add significant uncertainty to regional and global growth.
Domestic economic policies, trade policies and technology transfers will also be shaped by foreign policy.